實作:以廣度優先搜尋解決拼圖問題
前言
以下的「拼圖問題」是將一個已經移動打亂過的拼盤,想辦法移動回原本樣子的問題。
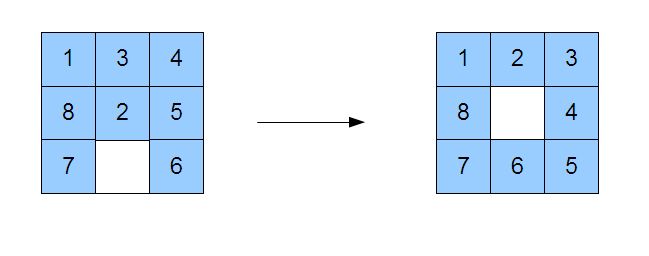
在以下程式中,我們用一個 3*3 的陣列來代表拼盤,並且用數字 0 來代表其中的空格,因此將方塊 2 移動到空格,其實是用將 0 與 2 兩個數字位置交換所達成的。
透過這樣的資料結構,我們就可以用「廣度優先搜尋」(BFS) 來解決拼圖問題了,以下是我們用 JavaScript 實作,並用 node.js 進行測試的結果。
程式實作:拼圖問題
檔案:puzzleSearch.py
from copy import deepcopy
def enqueue(a, o):
a.insert(0,o)
def dequeue(a):
return a.pop()
def findXY(board, value):
for x in range(len(board)):
for y in range(len(board[x])):
if board[x][y] == value:
return x,y
return None
def boardClone(b):
return deepcopy(b)
def board2str(b):
rows = []
for row in b:
rows.append(str(row))
return '\n'.join(rows)
def swap(b,x1,y1,x2,y2):
x2 = round(x2)
y2 = round(y2)
if x2<0 or x2 > 2 or y2<0 or y2>2:
return False
t = b[x1][y1]
b[x1][y1]=b[x2][y2]
b[x2][y2]=t
return True
def move(board, dir): # 加入所有可能的移動方式
x,y = findXY(board, 0) # 找出空格 0 的位置
nboard = boardClone(board)
s = False
if dir == 'up':
s=swap(nboard,x,y,x-1,y) # 空格和上面一格交換
elif dir == 'right':
s=swap(nboard,x,y,x,y+1) # 空格和右邊一格交換
elif dir == 'down':
s=swap(nboard,x,y,x+1,y) # 空格和下面一格交換
elif dir == 'left':
s=swap(nboard,x,y,x,y-1) # 空格和左邊一格交換
return nboard if s else None
def moveAdd(board, dir, neighbors): # 向 dir 方向移動,並加入到 neighbors 陣列中
nboard = move(board, dir)
if nboard != None:
neighbors.append(nboard)
def getNeighbors(board): # 取得所有鄰居
neighbors = []
moveAdd(board, 'up', neighbors)
moveAdd(board, 'down', neighbors)
moveAdd(board, 'right', neighbors)
moveAdd(board, 'left', neighbors)
return neighbors
def bfs(q, goal): # 廣度優先搜尋
while len(q) > 0:
node = dequeue(q) # 否則、取出 queue 的第一個節點。
nodestr = board2str(node)
if node == goal: return True
if visited.get(nodestr) == None: # 如果該節點尚未拜訪過。
visited[nodestr] = True # 標示為已拜訪
else: # 否則 (已訪問過)
continue # 不繼續搜尋,直接返回。
neighbors = getNeighbors(node) # 取出鄰居。
for n in neighbors: # 對於每個鄰居
nstr = board2str(n)
if visited.get(nstr) == None:# 假如該鄰居還沒被拜訪過
parent[nstr] = nodestr
level[nstr] = level[nodestr] + 1
enqueue(q, n) # 就放入 queue 中
return False
def backtrace(goal):
print('======= backtrace =========')
nodestr = board2str(goal)
while nodestr != None:
print('{}\n'.format(nodestr))
nodestr = parent.get(nodestr)
goal = [[1,2,3],
[8,0,4],
[7,6,5]]
start= [[1,3,4],
[8,2,5],
[7,0,6]]
queue=[start] # BFS 用的 queue, 起始點為 1。
visited={}
parent={}
level={}
level[board2str(start)]=0
found = bfs(queue, goal) # 呼叫廣度優先搜尋。
print('bfs:found=', found)
if found:
backtrace(goal)
執行結果
mac020:04-graphSearch mac020$ python3 puzzleSearch.py
bfs:found= True
======= backtrace =========
[1, 2, 3]
[8, 0, 4]
[7, 6, 5]
[1, 0, 3]
[8, 2, 4]
[7, 6, 5]
[1, 3, 0]
[8, 2, 4]
[7, 6, 5]
[1, 3, 4]
[8, 2, 0]
[7, 6, 5]
[1, 3, 4]
[8, 2, 5]
[7, 6, 0]
[1, 3, 4]
[8, 2, 5]
[7, 0, 6]
結語
在上述執行結果中,我們是將盤面拼完後,才逆向追蹤印出移動過程,因此整個移動方法應該從最下面的盤面看起。換句話說,真正的順序如下:
1,3,4 1,3,4 1,3,4 1,3,0 1,0,3 1,2,3
8,2,5 => 8,2,5 => 8,2,0 => 8,2,4 => 8,2,4 => 8,0,4
7,0,6 7,6,0 7,6,5 7,6,5 7,6,5 7,6,5
從上面過程中,您可以看出我們的程式將打亂的盤面給拼回來了。
【本文由陳鍾誠取材並修改自 [維基百科],採用創作共用的 [姓名標示、相同方式分享] 授權】